Federated Semi-supervised Medical Image Classification via Inter-client Relation Matching
As a partial fulfillment for Visual Computing, CS6450
This paper deals with a very serious yet very common problem of intracranial hemorrhage detection using CT scans as input image. That is in plain terms, this paper tries to detect brain attacks also known as brain strokes by looking at their CT scans. It is estimated that one person in the world dies from stroke every 10 seconds. Stroke causes the death of 6.2 million peoples every year worldwide and it is predicted that there will be about 3.3 million cases of stroke in India itself by 2030. It is very surprising to know that it kills more people than HIV, Tuberculosis, and Malaria combined, with a fact that it is the second most common cause of mortality and third most common cause of disability in the world.
For the same, Medical institutions across the world have started collaborating to develop a model with the same detection objectives. Medical information are sensitive and private to share but unfortunately the any machine learning model needs a lot of information to learn. So, we have a problem here.
Talking about the traditional approaches, Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a privacy-preserving solution for this, which allows to learn from distributed data sources by aggregating the locally learned model parameters without exchanging the sensitive health data. The parameters for the models are learned at the client location using the data that are available to them. Once, the model learns, the learned parameters of the models are the shared back to the central server. Such parameters from N different distributed clients are aggregated to get the global parameters which is now used for making inferences.
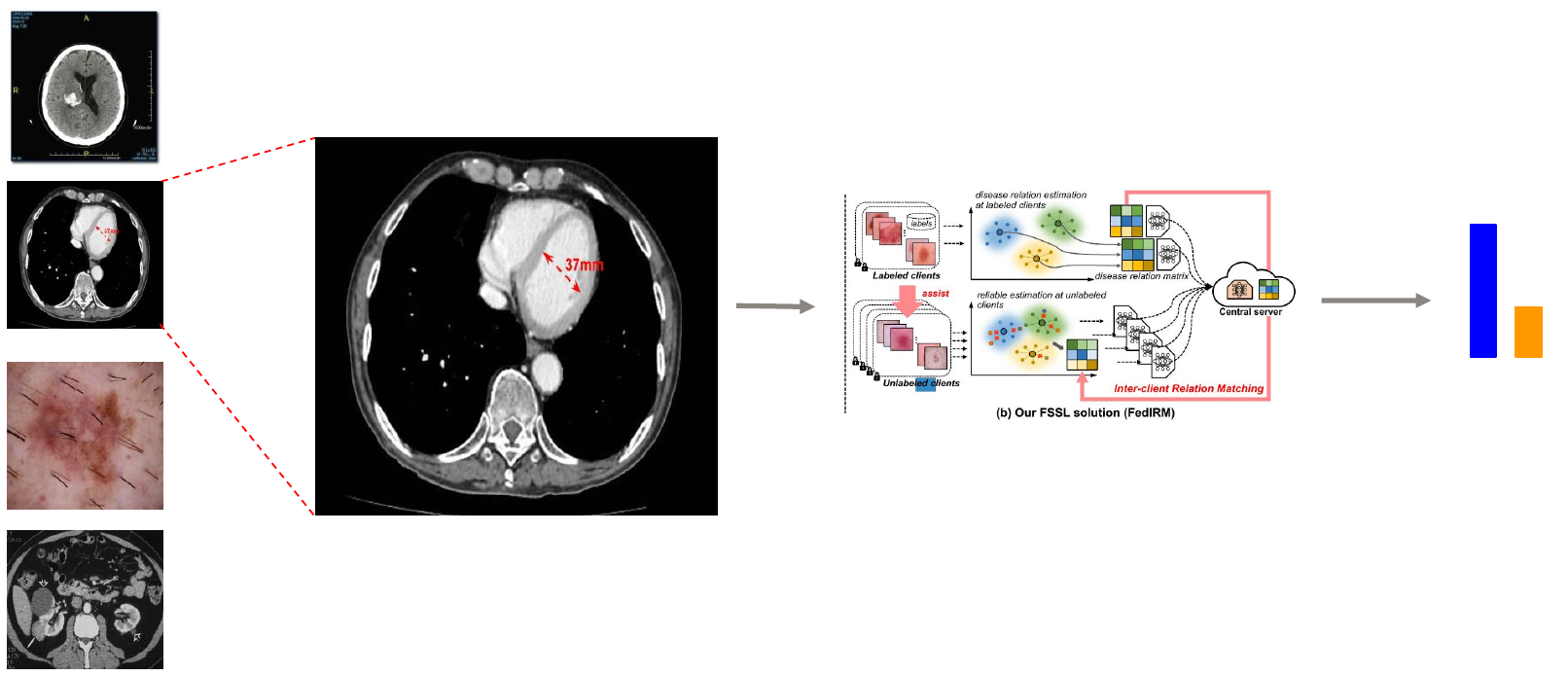
A crucial point to note in this federated setting is that, the local learning at the client side is based on the Supervised setting meaning there is a definite class label associated with all the present CT scans indicating the presence or absence of intracranial hemorrhage.
But in practical scenarios annotations of such scans is a very expensive and time consuming task which is not always possible. Because of the same there are a huge number of clients that cannot contribute to a proper learning of the model.
Hence this paper explores semi supervised approach to utilize unlabelled scanned images or unlabelled clients to train the model for better learning. A naive solution is to simply integrate the off-the-rack semi-supervised learning (SSL) methods onto the federated learning paradigm.
But semi supervised setting relies heavily on the assumption that the labeled data is accessible to provide necessary assistance for the learning from unlabeled data which in our scenarios is not achievable as we have clients that are entirely unlabelled.
To elaborate on the same, in a supervised setting a model learned from labelled images is used to predict the pseudo labels for unlabelled clients. Then the same model is trained using those pseudo labels, successfully making the use of the unlabelled data.Now talking about the federated learning paradigm,
Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a privacy-preserving solution for this, which allows to learn from distributed data sources by aggregating the locally learned model parameters without exchanging the sensitive health data.
The proposed model has some sort of a teacher model that learns from the labelled clients in supervised setting and uses his knowledge of the task in hand to teach a student model at the unlabelled setting to discriminate between CT scans having hemorrhage or not. This way a combined model from both of them will be able to use data be it either labelled or unlabelled mitigating any scarcity or distribution of medical images.
In our training scenarios, the labelled clients are completely separate from the unlabelled ones. Now the question becomes how to build an interaction system between the learnings at the labeled clients and undirected learnings at the unlabeled clients, or how to share the knowledge between the two clients given the challenging constraint of data decentralization between multiple clients.
Hence the proposed approach,
Following the same trend of thought, This paper explores a novel approach of inter client relation matching in which the learnings at labelled client are distilled down to a single representation matrix called the disease relation matrix which is used as a pseudo label for training at the unlabelled client side. This approach connects the learning of the labelled client across the unlabelled clients promoting the task of discrimination or classification using the unlabelled samples. In simple words labelled clients assists the unlabelled clients to learn the classification problem properly.